Kidney
Here are my notes from my former website wizardofeyez.com. The IBIS software I collaborated on is now available for free, though the website seems to be down recently…
Chronic Kidney Failure
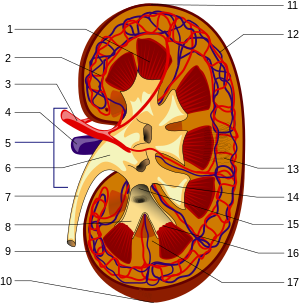
Structures of the kidney: 1.Renal pyramid 2.Interlobar artery 3.Renal artery 4.Renal vein 5.Renal hilum 6.Renal pelvis 7.Ureter 8.Minor calyx 9.Renal capsule 10.Inferior renal capsule 11.Superior renal capsule 12.Interlobar vein 13.Nephron 14.Minor calyx 15.Major calyx 16.Renal papilla 17.Renal column (no distinction for red/blue (oxygenated or not) blood, arteriole is between capillaries and larger vessels (Photo credit: Wikipedia)
The following summary was compiled by Dr. Glen Swartwout using the IBIS database of alternative medicine research. The program is available to licensed or certified health practitioners. Research summaries on specific topics may be requested with a donation to the Remission Foundation. For individualized recommendations, ask for a Biofield Analysis.
Definition
A disorder of the kidneys resulting from many pathologic conditions that cause abnormal and insufficient functioning and excretion of the kidneys.
Etiology
There are 3 stages of chronic kidney failure (CKF): decreased renal reserve, renal failure, and uremia. The most common cause for CKF is glomerulonephritis, but other frequently seen precipitating factors are diabetes mellitus, polycystic kidney disease, hypertension, nephrosclerosis, as well as assorted other reasons. The glomerular filtration rate must be significantly reduced before symptoms of CKF appear.
In the early stages of CKF, when the GFR is only 35-50% of normal, the patient is totally asymptomatic, and due to renal functional adaptation, the renal indices are well maintained.
When the GFR reaches 20-35% of normal azotemia will begin, and although patients are still usually pretty symptom-free, the renal reserve is compromised to the point that any additional stress (infection, dehydration) can usher in overt failure.
Overt CKF: with the systemic manifestations of uremia: is typically seen when the GFR decreases to below 20-25% of normal (GFR < 6 ml/min./sq. m).
Signs and symptoms
- Patients may be asymptomatic or may experience only mild and vague symptoms even when the BUN and creatinine are elevated.
- Nocturia.
- Fatigue.
- Lethargy.
- Diminished mental sharpness.
- Neuromuscular presentations: muscle twitching/cramps, convulsions.
- GI presentations: anorexia, vomiting, stomatitis, offensive taste in the mouth.
- GI ulcers and bleeding: in advanced stages.
- Malnutrition with muscle wasting: in advanced disease.
- Skin: may become yellow-brown, itching may be severe, may develop a “uremic frost” (urea from the sweat crystallizing on the skin).
- Hypertension.
- Many other signs and symptoms ranging from sexual dysfunction, to headache, to ecchymoses, to hepatitis, etc.
Lab findings
- Increased BUN and creatinine.
- Acidosis.
- Normochromic normocytic anemia.
- Loss of renal concentrating ability specific gravity usually equals glomerular filtrate (<1.020).
- Decreased urine osmolality.
- Decreased urine volume in dilution test.
- Abnormal U/A: proteinuria, hematuria, pyuria, casts.
- Decreased serum sodium.
- Increased serum potassium.
- Decreased serum calcium.
- Increased serum phosphorus: when the creatinine clearance falls below 25 ml/minute.
- Increased or normal serum alkaline phosphatase.
- Increased serum magnesium when GFR falls below 30 ml/minute.
- Increased serum amylase.
- Possible increase in serum CK.
- Increased serum triglycerides, VLDL and cholesterol.
- Increase in blood organic acids: phenol, indoles, amino acids.
- (+) bleeding tendency.
- Decreased serum albumin and total protein.
- May see lab findings in regard to uremic meningitis or uremic pericarditis/pleuritis/pancreatitis, or other disorders.
Prognosis
Prognosis depends on the cause and severity of the primary disease and existing complications. Close attention to diet and protein/potassium/ liquid intake, dialysis, or transplantation are the conventional treatments.
Differential Diagnosis
- Determine underlying cause.
- Hepatic or cardiac failure.
- CNS infections.
Exercise
- ROM exercises of the trunk: to enhance renal circulation
Hydrotherapy
- fever treatments
- constitutional hydrotherapy
Manipulation
- spine: check and align T12, T10-L1.
- Chapman’s reflex: slightly lateral and superior to umbilicus, then between T12 and L1
- Spondylotherapy: concussion of T7 then T10, alternate dilation and contraction
Without hemodialysis
restrict protein to 10 g q.d., or eliminate totally. Glucose is infused or a nasogastric feeding is used. Severely restrict Sodium and Potassium.
With hemodialysis
- 60% carbohydrates
- 7-12% protein
- 28-33% fat
- diet high in complex carbohydrates: whole grains, vegetables and fruits
- low in proteins, and medium low in polyunsaturated and monosaturated fats
- Sodium is restricted to 500-1000 g q.d. depending on accompanying hypertension (see hypertension)
- Potassium is limited to 1.5-3.0 g q.d.
Therapeutic foods
apple peel tea (steeped), watercress, melons, greenbeans, potato broth, collards, beets, asparagus in small amounts, parsley in small amounts, grapes, foods that tonify the Kidney (Jensen, p. 63)
Fresh juices
- celery, parsley, and juniper berry tea (Jensen, p. 63)
- celery, parsley, and asparagus (Jensen, p. 52)
- carrot and parsley (Jensen, p. 52)
- pomegranate (Jensen, p. 52)
Foods contraindicated
asparagus and parsley with extreme kidney inflammation, rutabaga (Jensen)
Supplements
- Vitamin A 25,000 I.U. q.d.
- Vitamin C 1 g q.d.
- bioflavonoids 2 g q.d.
- Vitamin B-complex, especially B6
- Vitamin E 400 I.U. q.d. (Kirschmann, 1984)
Drug interaction
- Sodium, Potassium and triamterene (Dyrenium): triamterene increases urinary Sodium and reduces urinary Potassium (Austin)
- In patients on chronic dialysis; Vitamin D and heparin: heparin interferes with renal hydroxylation of Vitamin D. Note: this could lead to osteopenia, check 1,25(OH)2 cholecalciferol levels (Austin)
Herbs
- Apocynum cannabinum (toxic): uremia (Harper-Shove, p. 95)
- Barosma betulina: uremia (Harper-Shove, p. 95)
- Echinacea angustifolia: uremia with convulsions, chronic nephritis (Harper-Shove, p. 95; Weiss, p. 243)
- Lespedeza capitata: acute and chronic renal insufficiency, i.e. nephrosclerosis; reports of its efficacy vary (Weiss, p. 243)
- Orthosiphon stamineus: eliminates fluid, nitrogenous wastes, sodium chloride; possible ulcerations; chronic nephritis, early signs of decompensation and renal atrophy (Weiss, p. 240)
- Pilocarpus jaborandi (toxic): uremia, with convulsions (Harper-Shove, p. 95)
- Piper methysticum: uremia (Harper-Shove, p. 95)
Chinese Herbal formula
Wan Shi Niu Huang Qing Xin Wan (patent): Heat, including unconsciousness with fever (Naeser, p. 133) Acupuncture: After assessing the person and palpating, consider these patterns: Kidney Qi, Yang and/or Yin Xu (Deficiency); Heart Yin Xu (Deficiency)
Palpate and consider
- Bl-15 (+): calms the Heart and the Shen; strengthens Heart Qi, nourishes Heart Xue (Blood), and tonifies Heart Yin; invigorates circulation of the Qi and Xue (Blood) and tonifies Xu (Deficiency); Heart Shu Associated point
- Bl-20 (+): regulates Spleen Qi; tonifies the Spleen and Stomach to facilitate digestive transportation and transformation; benefits the Ying (Constructive) Qi; enhances Spleen Yang to mobilize Stagnant Qi; reverses Rebellious Stomach Qi; tonifies and harmonizes the Xue (Blood); nourishes and contains the Xue (Blood); warms the Middle Warmer (Æ); drains Heat Shi (Excess) from the Middle Warmer; resolves Dampness; provides strength to the extremities; Spleen Shu Associated point
- Bl-22 (+): regulates San Jiao collectively, and the Upper, Middle and Lower Warmers individually; tonifies the Kidney; eliminates Dampness and regulates passage of water in the Lower Warmer (diuresis); regulates the transforming function of Qi; Triple Warmer Shu Associated point
- Bl-23 (+): clears the Brain; strengthens Heart (Ross, 1985, p. 130); strengthens Qi Hai and regulates Kidney Qi; tonifies the Kidney and strengthens Yang; resolves Dampness; nourishes Yin, Xue (Blood) and Kidney Jing (Essence); Kidney Shu Associated point
- Bl-47 (+): tonifies Kidney Qi, Kidney Yang, Kidney Yin, Jing (Essence) and Yuan (Original) Qi; regulates the Water Pathways; facilitates urination; resolves Dampness; Kidney psychospiritual associated point
- Bl-26 (=): regulates the Lower Warmer; transforms Damp-Stagnation and resolves Damp-Heat; “relates to Kidney Yin” (Finkelstein, p. 45); alleviates polyuria; strengthens the spine, esp. lower back; lower lumbar associated point
- Bl-58 (+): promotes flow of Qi; strengthens Kidney function; increases stamina; eases low back pain; sedates pain; Kidney Luo Connecting point
- GV-4 (+): clears the Brain; relieves mental and physical exhaustion; nourishes the Yuan (Original) Qi; strengthens the Kidney; benefits and replenishes the Kidney Yang; frees the channels and invigorates the collateral vessels; consider moxa but not with predominantly Yin Xu (Deficiency) condition
- GV-3 (+): adjusts Kidney Qi; reinforces the Kidney; stimulates testes; regulates the Ren Mai (Conception Vessel) and Chong Mai (Penetrating Vessel)
- jing gong (+): tonifies Kidney Yang; warms the Jing (Essence)
- GB-25 (+): tonifies Kidney; sedates and/or warms Kidney Yang; influences Kidney Yin; clears and regulates Water Pathways; resolves Dampness; regulates Stomach; removes Qi Stagnation; invigorates the channels; Kidney Mu Alarm point
- Lu-7 (+): promotes sweating; opens and regulates the Ren Mai (Conception Vessel); regulates the Yin Qiao Mai (Yin Motility Vessel); stimulates Lung function of dominating Water Pathways; effects release of sexual hormones; promotes diuresis by descending the Turbid; Lung Luo Connecting and Exit point; Master point of the Ren Mai (Conception Vessel); Couple point of the Yin Qiao Mai (Yin Motility Vessel); takes Yuan (Original) Qi back to the Lung that has not been absorbed by the Yang Ming and therefore ensures the Qi feedback into the Kidney (Metal to Water) (Finkelstein, p. 3)
- CV-6 (+): tonifies Yuan (Original) Qi; warms the Lower and Middle Warmers; strengthens Kidney Xu (Deficiency); strengthens and moves the Qi; reinforces Jing (Essence); tonifies Kidney; benefits, nourishes and invigorates Kidney Yang; warms Ming Men (Life Gate Fire) (esp. with Æ); influences pituitary, thyroid and adrenals (Worsley, 1975, p. B-20); captures the Blood and stops bleeding (+); regulates Qi of Chong Mai (Penetrating Vessel) and Ren Mai (Conception Vessel); moves Qi and Xue (blood) in Lower Warmer; dispels Dampness
- CV-4 (+): pacifies the Shen; benefits Yuan (Original) Qi; nourishes Xue (Blood) and Yin; regulates the Qi; regulates and reinforces the Qi of the Chong Mai (Penetrating Vessel) and Ren Mai (Conception Vessel); separates the Clear and Turbid; regulates the Bladder; facilitates diuresis; nourishes and stabilizes the Kidney; strengthens and replenishes the Kidney Qi; stimulates testes and sex hormones; warms the Kidney Yang and the Lower Warmer; Small Intestine Mu Alarm point;
- Sp-9 (=): regulates and tonifies Spleen (especially Yang); regulates the Water Pathways; transforms Damp Stagnation, esp. through promotion of diuresis; dispels Damp-Heat and eliminates Phlegm-Dampness; benefits the Lower Warmer; Spleen Water point
- Sp-6 (+): pacifies the Shen; nourishes Yin, esp. of the Spleen, Liver and Kidney; clears Fire due to Xu (Deficiency); tonifies Qi and builds the Xue (Blood); aids transportation and transformation to improve digestion and nourishment; spreads the Liver Qi and suppresses Liver Heat; warms the Middle and Lower Warmers; restores circulation to the Lower Warmer; tonifies the Kidney; regulates the Bladder; transforms Dampness and Heat; facilitates diuresis; Jiao Hui Intersecting point of the three Foot Yin channels
- Kd-7 (+): clears Heat and nourishes Yin; tonifies Yuan (Original) Qi; regulates Kidney Qi; strengthens and enriches the Kidney; stimulates adrenals, thyroid and testes; regulates Bladder and Water Pathways; disperses Stagnation; strengthens the low back; Kidney Metal and Tonification point
- Kd-5 (+ or =): reinforces the Chong Mai (Penetrating Vessel) and Ren Mai (Conception Vessel); regulates Qi and Xue (Blood); strengthens Yuan (Original) Qi; strengthens function of Kidney; revives circulation of Qi in the Kidney organs and channels; moves the Lower Warmer; clears and regulates the Bladder; Kidney Xi Cleft Accumulation point
- Kd-3 (+): tonifies the Kidney, Yuan (Original) Qi, Xue (Blood) and Jing (Essence); strengthens the Brain; pacifies Xu (Deficiency) Fire; nourishes and enriches Kidney Yin, supplies Liver Yin, and tonifies Yin of the entire body; tonifies Kidney Yang; stabilizes Kidney Qi; strengthens control of ejaculation; regulates the Chong Mai (Penetrating Vessel) and Ren Mai (Conception Vessel); regulates the Water Pathways; Kidney Yuan Source and Earth point
- Lv-3 (-): clears head and thinking; promotes smooth flow of Qi and Xue (Blood); spreads Liver Qi Stagnation; subdues Liver Yang; suppresses Rebellious Qi to stop vomiting; calms Stomach and expands chest; tonifies Liver Xue (Blood); discharges Damp-Heat in the Lower Warmer; opens the channels and relaxes convulsions, spasms and cramps; Liver Yuan Source and Earth point; Independent Associated point for spasms Illustrative combinations:
- Bl-22, Bl-23, Bl-47, CV-3, CV-4 and CV-6 for kidney failure (Eisen)
- Bl-47, Kd-3 and GV-4: strengthen the Kidney (Finkelstein, p. 48)
- Homeopathics:
- Apis mellifica: thirstlessness; edema of face, extremities; pain in head, back, limbs, kidneys; scanty, frequent urination heavily loaded with albumin
- Apocynum cannabinum: edema with scanty urine and thirst
- Arsenicum album: watery diarrhea; pale skin; many urine casts; fear of death; convulsions
- Calcarea sulphurica: anemia with progressive emaciation and debility
- Cantharis: uremic delusions with sense of persecution; suppression of urine with restlessness, flushed face; urge to pass urine but none present in bladder
- Colchicum: kidneys produce no urine; scanty urine with edema; inky, dark brown to black urine; proteinuria
- Digitalis: degeneration of kidney with palpitation of heart, slow pulse
- Helleborus niger: uremia with unconsciousness; pupils dilated, insensitive to light; convulsions; strong urinous odor from body
- Plumbum metallicum: degeneration of kidney; pale, bloated, heavy expression
- Solidago: tenderness of kidneys to slightest touch with pain extending from kidney to abdomen; urine scanty, thick, voided with difficulty
- Terebinthina: early stages; urine bloody with pain along ureters and in the back
Flower Remedies
- rock rose
- agrimony
- gentian
- impatiens
- vervain (Chancellor, pp. 165, 193)
- chamomile
- blackberry (Gurudas, pp. 214, 234)
- gorse (Weeks, p. 95)
Color Therapy
- lemon (helps to dissolve blood clots; acts as a chronic alterative) on back
- magenta (the circulation system) on front
- scarlet (acts as a stimulant to the kidney and adrenals) on kidneys or magenta (the kidneys) blood pressure is too high (Dinshah, 1985, p. 85)